

- SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX HOW TO
- SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX INSTALL
- SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX UPDATE
- SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX SOFTWARE
- SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX CODE
When you end your SAS session, any libraries that you’ve defined will be lost. For example, if we have a dataset named sample stored in the folder ‘C:\Users\Research\Thesis’, which we’ve told SAS is the location of our library called practice, then we refer to that dataset as practice.sample The second part of the name (after the period) is the dataset’s name. The first part of the name (before the period) is the dataset’s library assignment. Once a library has been assigned to a location with a SAS dataset, the dataset can be referred to in statements using two parts: libref.SAS-dataset-name You will get an error message if you try to refer to a dataset that has not yet been pointed to in a LIBNAME statement. Most SAS users put their LIBNAME statements at the beginning of the program, but you can put a LIBNAME statement anywhere in the program as long as it comes before you reference a file in that location. (This folder must already exist on your computer.) Here is an example LIBNAME statement that creates the library named practice and assigns it to a folder in the directory ‘C:\Users\Research\Thesis.’ LIBNAME practice 'C:\Users\Research\Thesis' Finally, the text in quotes is what path name you tell SAS to assign the library to. It must be eight or less characters and start with a letter. The second word ( libref) is what you name the library. Here the first word ( LIBNAME) is the SAS keyword that tells it to create a library. The format of the LIBNAME statement is: LIBNAME libref 'Folder path name here' A LIBNAME statement is one of those global statements that we mentioned in Section 1 that does not occur in a data step or a proc step. A library is assigned a location with a LIBNAME statement in SAS. One or many datasets can be assigned to the same library.

Alternatively, you can create your own data in SAS, which is also covered below. If it is stored as a file other than SAS (Excel, SPSS, text, etc.) then you’ll need to help SAS read it with one of the methods described in the next sections of this tutorial. If the data you want to work with is already a SAS dataset stored somewhere on your computer, then all you need to do to start working with your data is assign a library name to the location of the dataset. SAS libraries allow users to safely store things like data sets and user-defined formats so that they can be accessed without having to reload or re-read them from an external file every time SAS is started. No issues so far with that either.A SAS library is a folder located on a user's disk drive or on the internet that is specially designated for use by SAS. I'm using a folder in my Google Drive to act as my library location. I bookmarked the required extension ( To run in future I just need to boot up the virtual machine, minimize it and hit up my bookmark in Chrome.
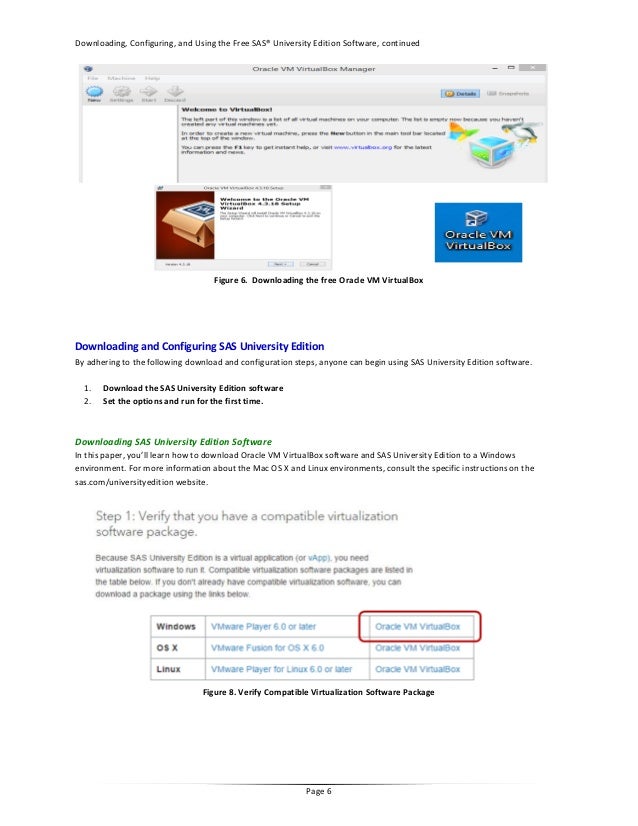
I should also add, running the program itself is handled by your local browser.
SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX CODE
Code editing and running, including autocomplete syntax support and some shortcut keys like F3 for running programs were all present. I didn't try anything outside using the sashelp library.
SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX SOFTWARE
SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX INSTALL
SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX UPDATE
Requested to update below in the comments as I said I#d give it a go. R-bloggers - blog aggregator with statistics articles generally done with R software.
SAS UNIVERSITY EDITION FOR VIRTUAL BOX HOW TO
Homework questions are for r/homeworkhelp How to ask a statistics question Modmail us if your submission doesn't appear right away, it's probably in the spam filter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
